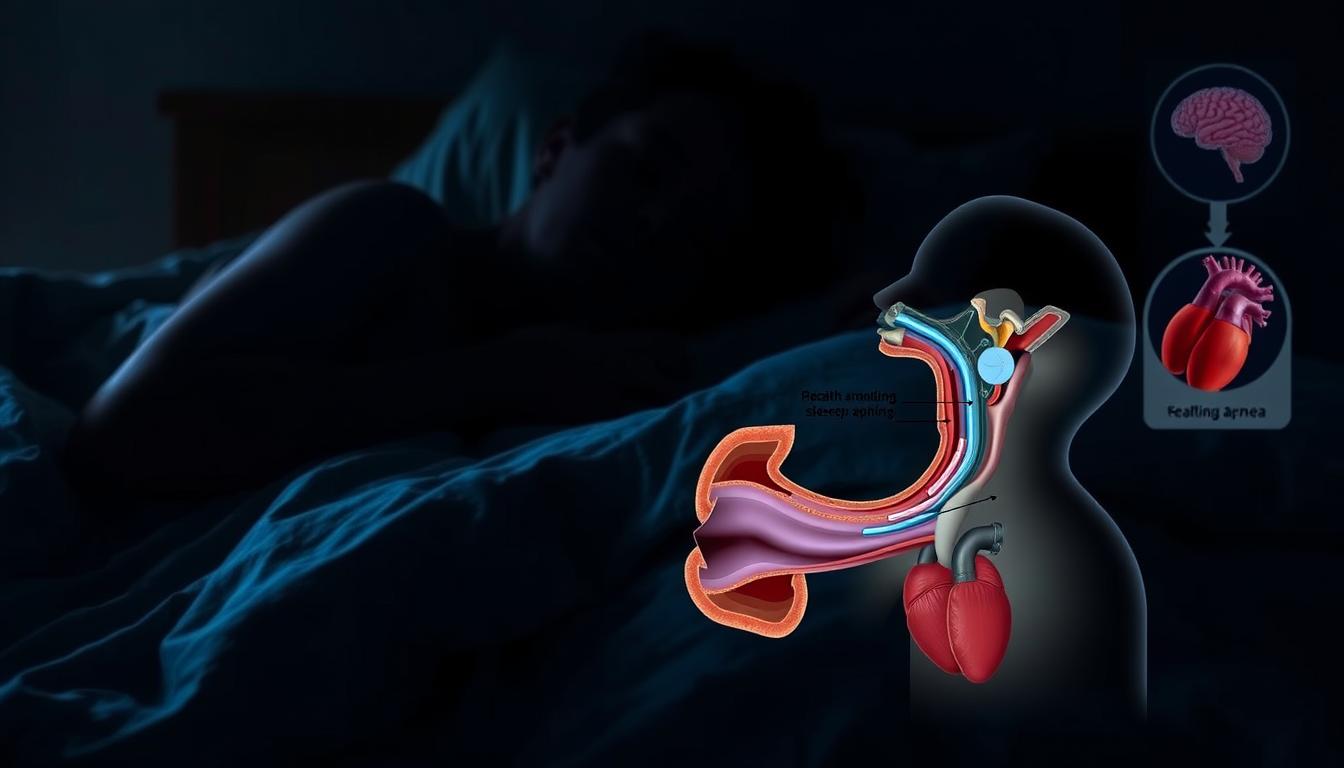
Snoring is often seen as just a minor annoyance. But, it can be a sign of a more serious problem. Sleep issues like sleep apnea can have big health risks if not treated.
Studies show that undiagnosed sleep apnea can raise the chance of heart disease and feeling tired during the day. It’s key to know the dangers of snoring to work towards better sleep.
Looking into the connection between snoring and sleep apnea helps us see why we must tackle sleep problems.
Key Takeaways
- Snoring can be a sign of an underlying sleep disorder.
- Sleep apnea is a potentially serious health condition.
- Untreated sleep apnea can lead to significant health risks.
- Understanding the risks associated with snoring is crucial.
- Addressing sleep-related issues can improve overall health.
Understanding the Link Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea
Snoring and sleep apnea are closely linked, and knowing this is key to spotting health risks. Snoring is not just a simple annoyance; it can signal a serious condition that needs medical care.
What Causes Common Snoring
Snoring happens when air can’t flow freely through the nose and mouth. Several things can block this airflow, including:
- Obesity: Being overweight, especially around the neck, can make the airway narrower, leading to snoring.
- Anatomy of the Mouth: The shape and size of your mouth, throat, and nasal passages can affect airflow, making snoring more likely.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, drinking alcohol, and some medications can relax throat muscles, causing snoring.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back can cause your tongue and soft palate to block airflow.
These factors can make the tissues in your throat vibrate, causing the sounds of snoring.
When Snoring Signals Something Serious
While snoring might seem harmless, it can also be a sign of sleep apnea. This is when a person stops breathing for short times during sleep. Symptoms that show snoring might be linked to sleep apnea include:
- Pauses in Breathing: Stopping breathing during sleep, followed by loud snorting or gasping.
- Daytime Fatigue: Feeling tired or groggy in the morning, even after a full night’s sleep.
- Morning Headaches: Often waking up with headaches, possibly from not getting enough oxygen at night.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing or paying attention during the day.
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, seeing a healthcare professional is crucial for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Snoring Could Be a Sign of This Silent Danger: Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that can harm your health. It causes pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep. These pauses can happen many times a night, messing up your sleep.
Sleep apnea is not just a simple sleep issue; it’s a condition that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. It’s often linked to snoring, but not everyone who snores has sleep apnea, and not everyone with sleep apnea snores.
Types of Sleep Apnea Explained
There are three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common form, caused by a blockage of the airway, usually when the soft tissue in the throat collapses during sleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This type occurs when the brain fails to send the appropriate signals to the muscles that control breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, this is a combination of OSA and CSA.

How Sleep Apnea Disrupts Your Body
Sleep apnea can have far-reaching effects on the body, including oxygen deprivation and sleep fragmentation. When breathing is paused or shallow, the body, or parts of it, may not receive enough oxygen. This can lead to various health issues.
| Health Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Oxygen Deprivation | Reduced oxygen levels can strain the cardiovascular system and other organs. |
| Sleep Fragmentation | Frequent awakenings can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to daytime fatigue. |
| Cardiovascular Risks | Increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. |
Understanding the risks associated with sleep apnea is crucial for managing the condition and mitigating its effects on overall health.
Health Risks and Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Untreated sleep apnea, often signaled by snoring, can have devastating health consequences. It’s not just a sleep disorder. It’s a potential precursor to more serious health issues that can significantly impact one’s quality of life and even be life-threatening.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Sleep apnea is closely linked with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. This includes hypertension, heart failure, and stroke. The repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep can lead to fluctuations in blood oxygen levels, putting a strain on the cardiovascular system.
- High Blood Pressure: The frequent awakenings and lack of quality sleep can lead to increased blood pressure levels.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Sleep apnea is associated with metabolic syndrome. This is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: The stress on the heart from sleep apnea can lead to irregular heartbeats.
Daytime Symptoms and Quality of Life Impact
The effects of sleep apnea are not limited to nighttime. Daytime symptoms can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Common symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and mood disturbances.
- Impaired Cognitive Function: Lack of quality sleep can affect memory, attention, and decision-making skills.
- Mood Disturbances: Irritability, depression, and anxiety are common among those suffering from untreated sleep apnea.
- Reduced Productivity: Excessive daytime sleepiness can impact work performance and daily activities.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
It’s crucial to recognize the warning signs that necessitate immediate medical evaluation. If you or someone you know experiences severe daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, or pauses in breathing during sleep, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Choking or Gagging during sleep.
- Morning Headaches that persist.
- Confusion or Disorientation upon waking.
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly mitigate the health risks associated with sleep apnea. Don’t ignore these warning signs; seek medical help to improve your quality of life and prevent potential complications.
Conclusion: Diagnosis and Treatment Options
It’s important to know how snoring and sleep apnea are connected. If you snore a lot, see a doctor to check your health.
To find out if you have sleep apnea, doctors use sleep studies and questionnaires. These help figure out how bad it is. A sleep study watches your body while you sleep to see if you stop breathing.
After finding out you have sleep apnea, treatment depends on how bad it is. For mild cases, losing weight and sleeping on your side can help. For more serious cases, a CPAP machine is often used. You might also try oral appliances or surgery to open your airway.
Getting medical help is the first step to dealing with sleep apnea. Knowing how to diagnose and treat it can help you feel better and live a healthier life.